Normal Ecg Values Chart
Look carefully and memorize the regular PQRST shape Heart Rate Normally should be between 60 100 Beatsmin.
Normal ecg values chart. In infants with heart rates in the range 100150 beatsmin one would expect the PR interval to be within the range 80110 ms extending in occasional individuals to 150 ms. Its description is therefore quite lengthy. P-wave amplitude should be 25 mm all leads.
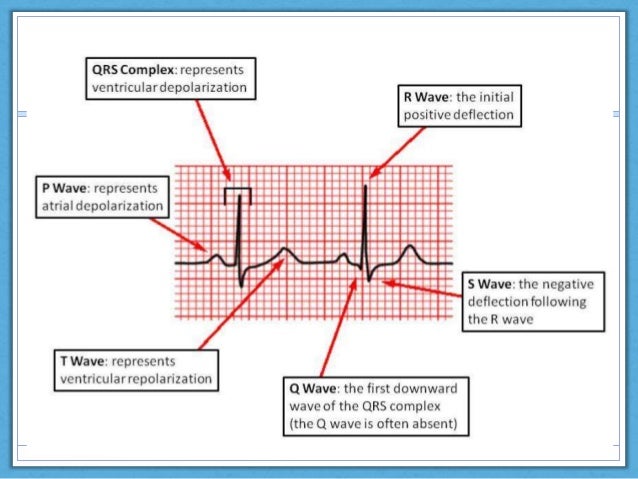
1P1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Causes. Normal values are based on computerized analysis of more than 15000 ECGs. The P wave 008011 seconds 23 small squares PR interval 011020 seconds 35 small squares QRS complex 006011 seconds 1525 small squares QT interval 036044 911 small squares.
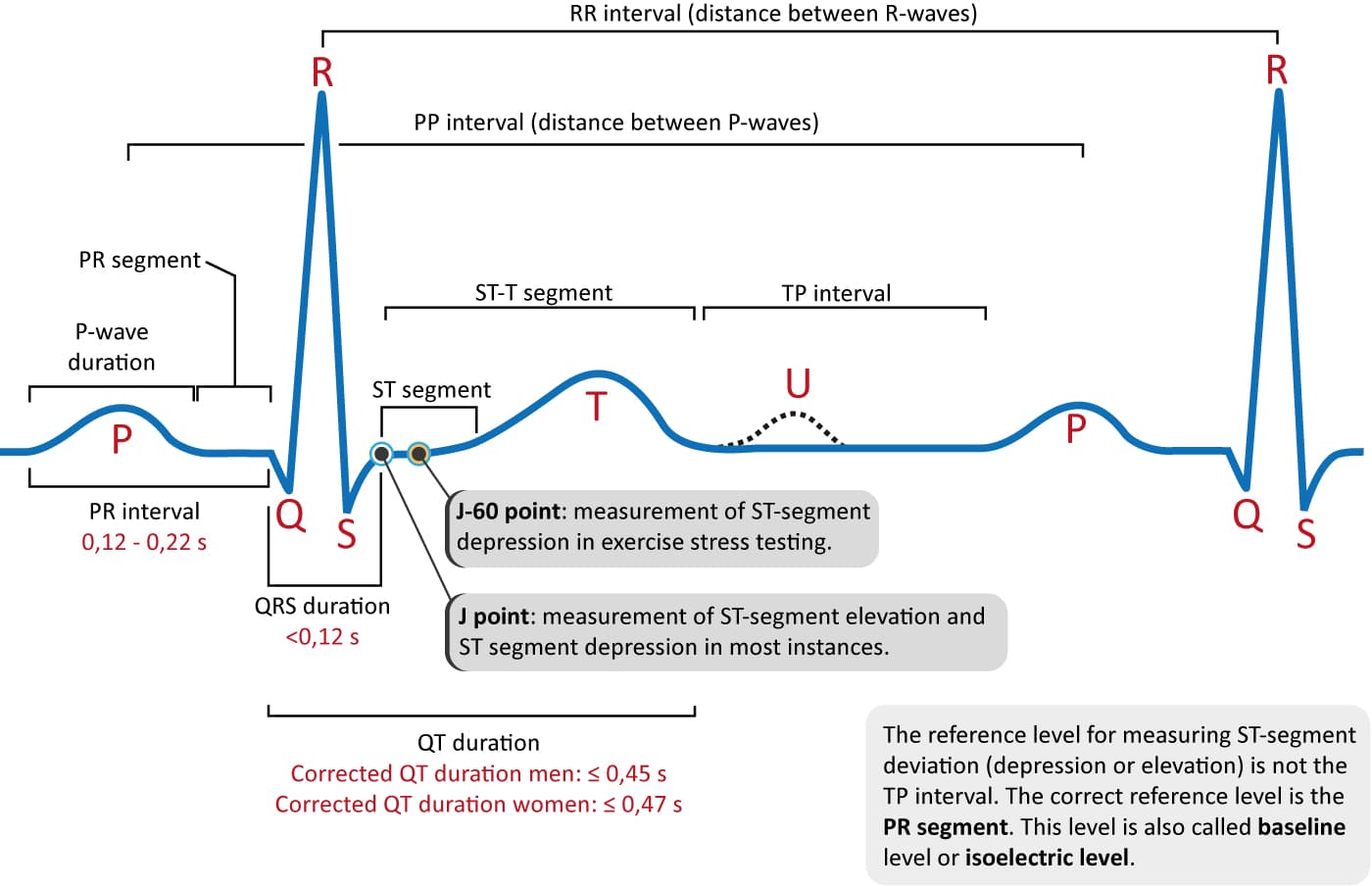
P-wave may be biphasic diphasic in V1 the negative deflection should be. Figure 712 A Drawing showing the location of the J point. How to read an EKG.
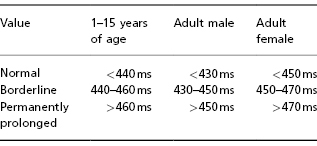
PR interval must be 012022 s all leads. 172002 21352 PM. 015 to 025 sec at normal heart rate.
Jet density and contourCW. 6 rows A normal heart rhythm contains a P wave a QRS and a T wave³ Knowing the normal amplitude. The purpose of this Web Page is to provide a reliable set of normal values for use in research and education.
Rhythm Sinus Atrial Supraventricular Junctional Ventricular. A standard ECG is recorded at 25mmsec and with a frequency cut off of no lower than 150Hz in adults and 250Hz in children. Jet area-central jets cm 2 5.
PISA radius cm ψ. The 12 lead ECG. Rate Q-T interval Width.
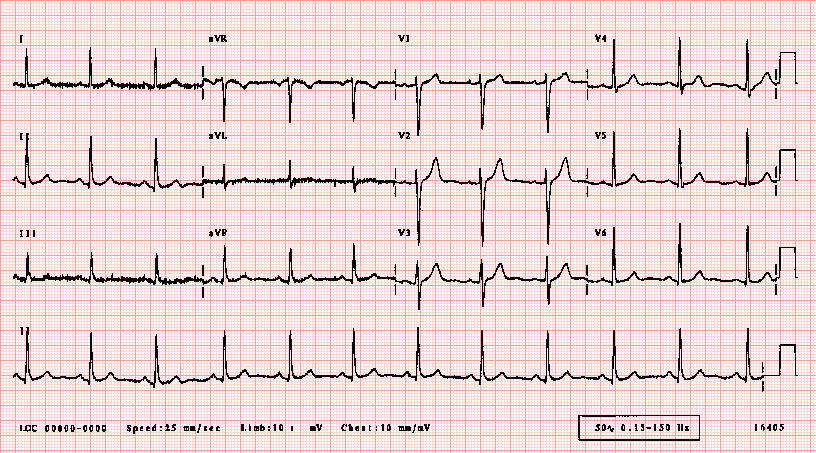
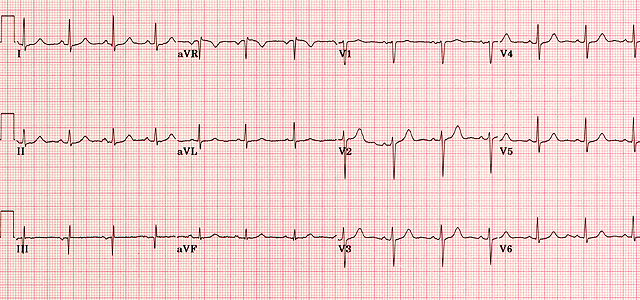
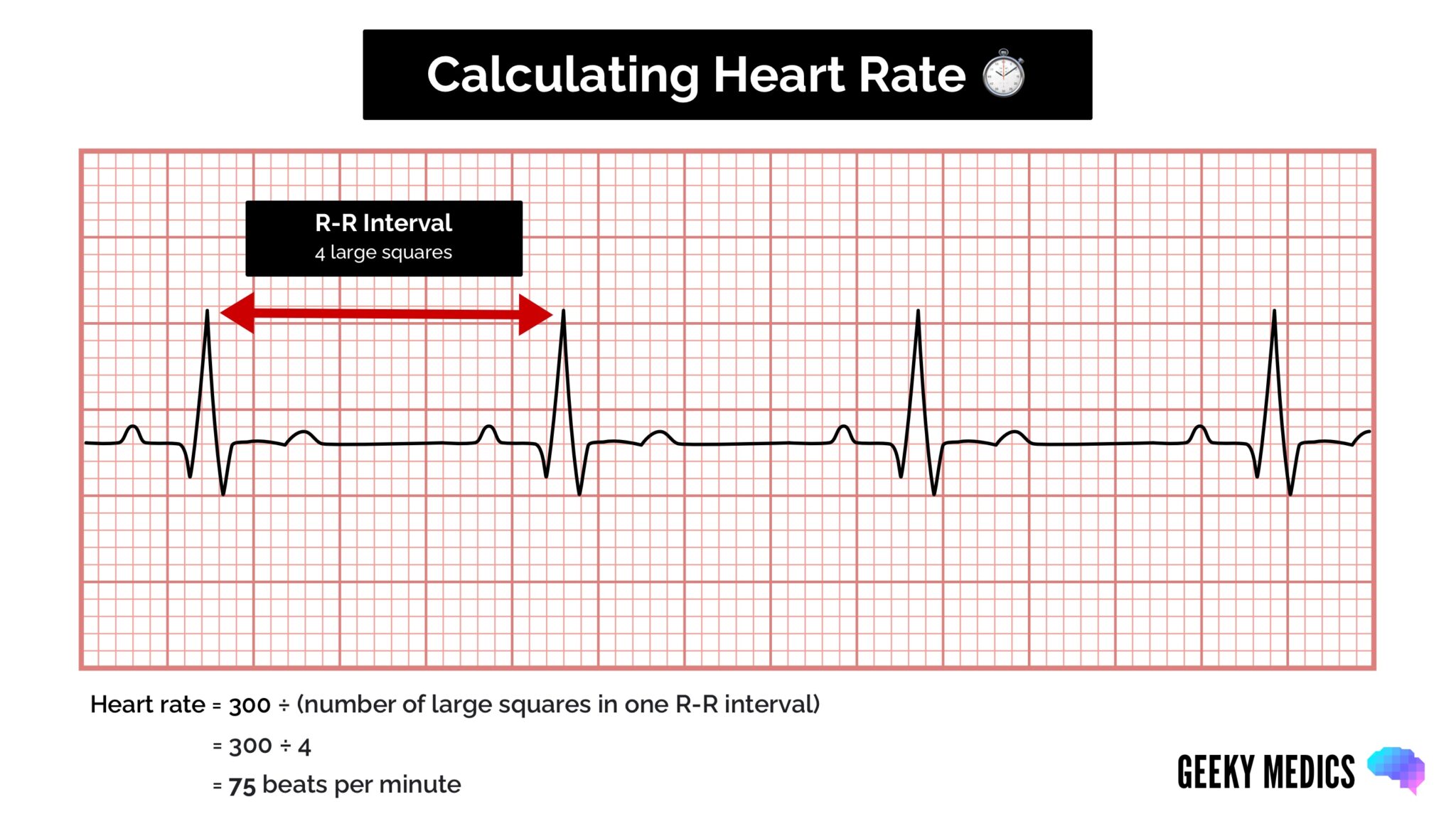
1 small square on an ECG trace at 25 mms speed 004 s. A normal ECG is illustrated above. A normal healthy individual usually has an ECG chart as the following.
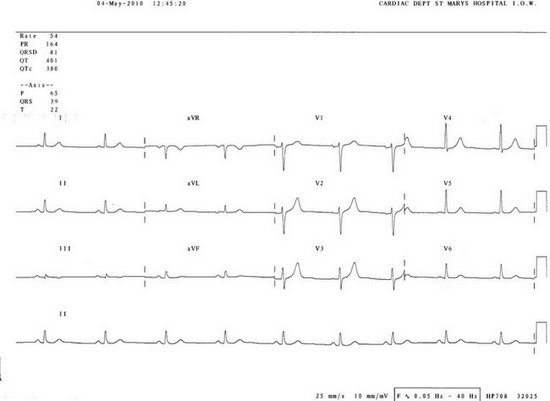
Time interval from the onset of QRS to the peak of R in V5V6 and in V1 are 0045 s and 002003 s respectively. The diagnosis of the normal electrocardiogram is made by excluding any recognised abnormality. This site provides a comprehensive overview of normal values for the adult and the pediatric electrocardiogram ECG covering the whole range of ages from the very young to the very old.
Normal adult 12-lead ECG. Previous normal ranges for the ECG have inadequately or inaccurately accounted for the large variations or normal based upon age and sex. VC width cm Φ.
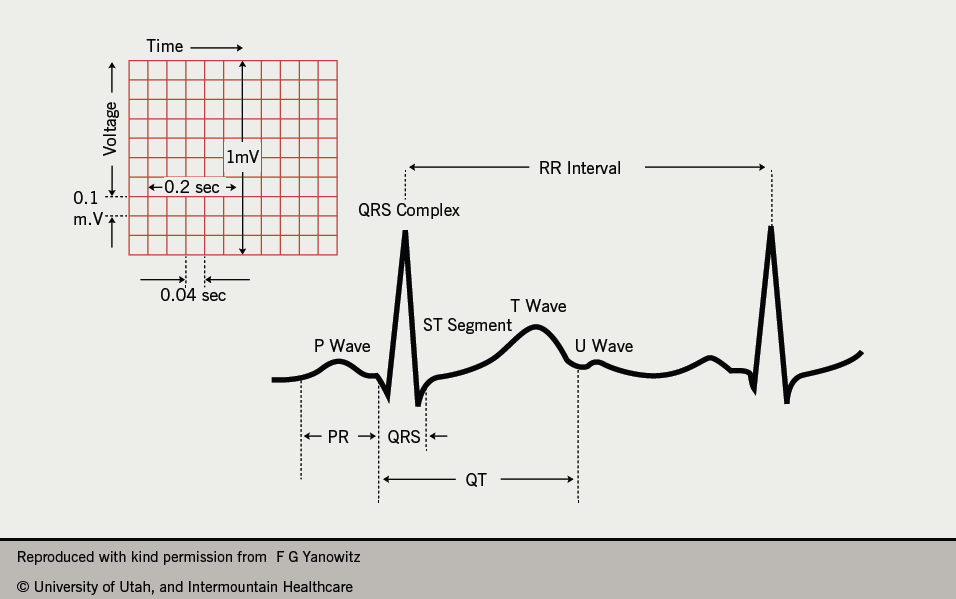
How to read an EKG The paper Up and down 1 box 01 mV Across 1 box 4 ms The rate 10 seconds per page. The tables accessible below were derived from 79743 subjects screened for participation. Whats what in an ECG The basics of ECG analysis.
004 010 second PqRs. Normal duration of less than or equal to 011 seconds. P-wave must be positive in lead II otherwise the rhythm cannot be sinus rhythm.
It may have a prominent second hump in the inferior limb leads. How to read an EKG P wave. EKG Flash Chart Created Date.
On the standard ECG paper with standard calibration the squares represent. P wave rate 60 - 100 bpm with. 012 -0 20 second consistent qRs.
How to read an EKG The Waveform. R- R P waves. Upright in leads I aVF and V3 - V6.
Note that the heart is beating in a regular sinus rhythm between 60 - 100 beats per minute specifically 82 bpm. Not defined but 07 07. Return to Technical Skills Home.
B The J point arrow in an ECG tracing. 7 rows Normal range. 197 beatsmin Cat P wave.
Approach to the ECG. Each P wave is followed by a QRS. In teenagers with slower heart rates the upper limit of normal would be around 180 ms.
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example Normal Sinus Rhythm NSR Rate. 120 to 240 beatsmin Mean. How to read an EKG PR segment.
These values are published. The standard calibration signal will look like this. A comprehensive overview of normal limits for the electrocardiogram.
Normal 60 100 Bradycardia 60 Tachycardia 100. All the important intervals on this recording are within normal ranges. The normal values of intrinsic deflection time IDT.
This will be present at the beginning or end of all four rows of the trace and shows. 60-100 per minute Rhythm.