Muscle Fiber Types Chart
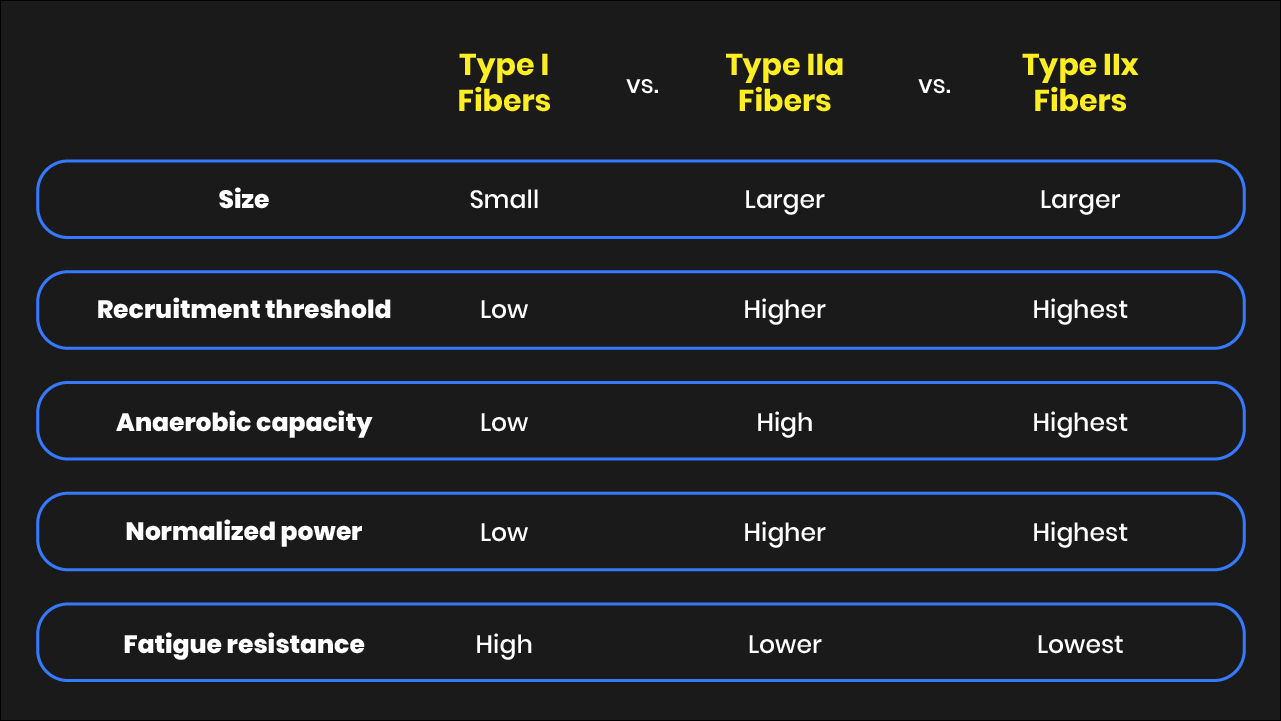
Fast-twitch muscle fibers can also be further categorized into type IIa and type IIbIIx muscle fibers.
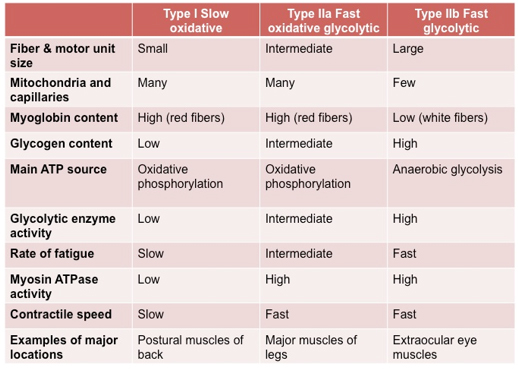
Muscle fiber types chart. Using these criteria there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers recognized Table 1. Skeletal muscles consist of two different muscle fiber types. In mouse an additional fast fiber type 2B blue is present.
Muscle fiber type I slow twitch or ST fibers Muscle fiber type II fast twitch or FT fibers which can be subdivided into type IIa and type IIb. The two types of skeletal muscle fibers are slow-twitch type I and fast-twitch type II. Type 2 muscle fibers also called fast-twitch on the other hand are much more fatigable but also much more powerful.
Thus the SOL muscles of C57BL6J mice. Relative to type I fibers type II fibers receive nerve signals and contract more quickly but contract for shorter periods and fatigue more quickly. Slow twitch Type I muscle.
Slow-twitch muscle fibers support long distance endurance activities like marathon running while fast-twitch muscle fibers support quick powerful movements such as sprinting or weightlifting. By the end of this video you will understand the three different muscle fibre types and have a memorable way of organizing the chart of characteristics. Type II or fast muscle fibers often appear white.
Different fiber types including type 1 red type 2A pink and type 2X purple can be intermingled within a single mammalian muscle. Fast oxidative FO fibers have relatively fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration to generate ATP. 10 rows Muscle fiber types can be broken down into two main types.
Slow oxidative SO fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration oxygen and glucose to produce ATP. SO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce low power contractions over long periods and are slow to fatigue. Slow-twitch muscle fibers type I and fast-twitch muscle fibers type II.
The thick are comprised of myosin and the thin are comprised of actin troponin and tropomyosin. FO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce ATP but produce higher tension contractions than SO fibers. Myofibrils long thin cylindrical rods usually 1-2 µm in diameter that run within and parallel to the long axis of the muscle fiber.
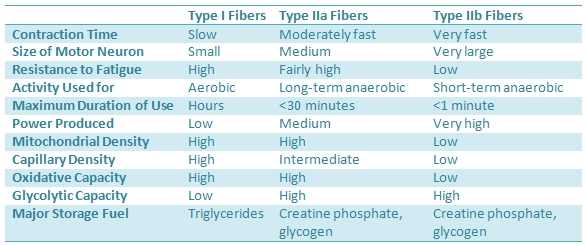
C Particular muscle groups can also be enriched for slow Soleus or fast extensor digitorus longus EDL muscle. First a brief primer on muscle fiber types. There are three types of muscle fibers.
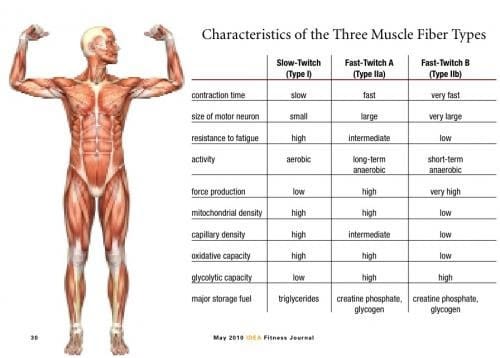
Type 1 muscle fibers also called slow-twitch fibers dont fatigue easily but theyre not very powerful. Muscle had type IIB 5442 811 IIDB 1937 298 IID 226 224 IIAD 1240 234 IIA 573. Muscle Fiber Type Comparison Chart.
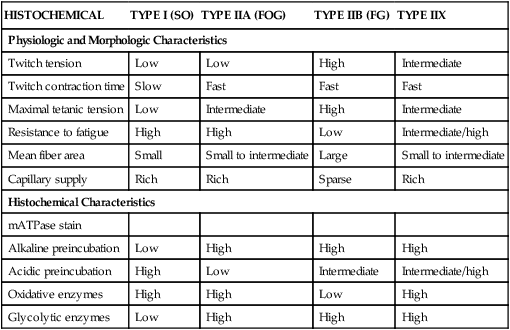
The chart reveals that slow oxidative fibers are not as strong as the other two but can be repeatedly used for extended periods of time without fatiguing which is essential for the endurance oriented athletes. Slow Oxidative Fast OxidativeGlycolytic and Fast Glycolytic. The chart above shows the differences among the three main muscle fiber types.
324 and I 574 255 fibers. Type I fibers primarily store energy as fatty substances called triglycerides. Type II muscle fibers primarily store energy as ATP and creatine phosphate.
RedFast slow-twitch or type I fibers RedSlow fast oxidative or type IIa fibers WhiteFast fast glycolytic or type IIb fibers.