H Nmr Peaks Chart
Cambridge Isotope Laboratories Inc.
H nmr peaks chart. For D 2O as a solvent the accepted reference peak δ 0is the methyl signal ofthe sodium salt of3-trimeth-. This is the easiest to interpret. Broad peaks and usually do not couple with neighboring protons typically they are broad singlets.
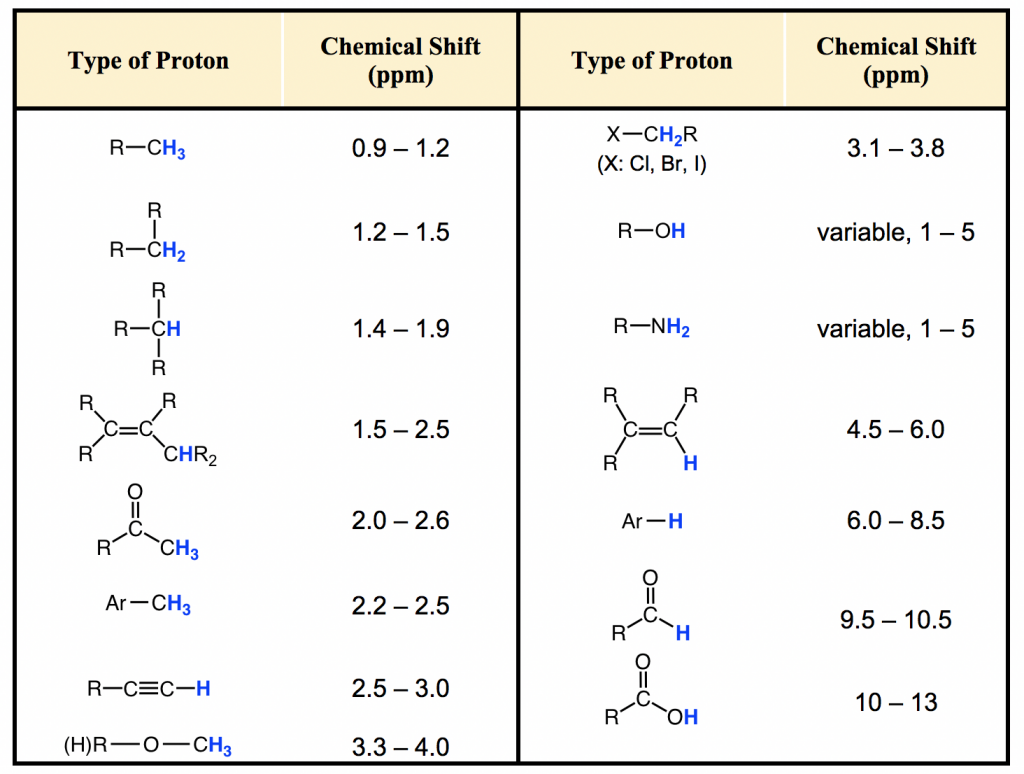
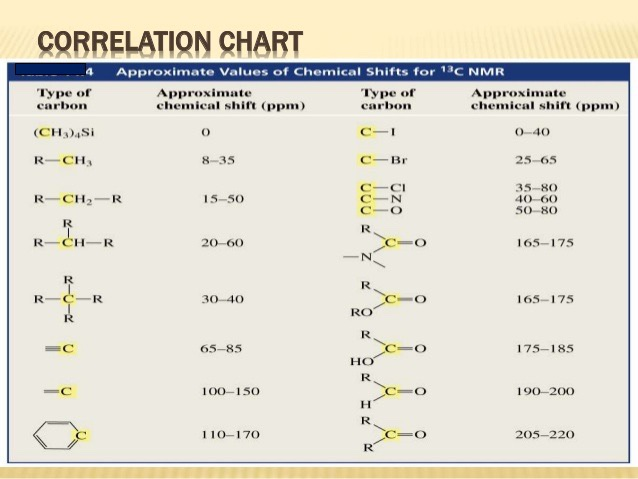
Chemical Shift Identity of neighbors. This page has tables of 1 H Chemical Shifts and 13 C Chemical Shifts. 46 C2H50 Z 427 582 53-55 Cl-13 560 50 56 512 468 58 49 591 64 62-64 51-54 CH3 59 C2H50 Z 612 Cl CH3 559 595 Down Field.
This chart shows the frequancies of protons that are attached to carbons. The number of peaks correspond to the number of unique or chemically indistinguishable hydrogen nuclei. Except where indicated the coupling constants and therefore the peak shapes are essentially solvent-independent and are presented only once.
600 MHz for 1H ppm 600 Hz 150 MHz for 13C. The two peaks on the spectrum are located at d242 and d107. C13 NMRs are often acquired as decoupled spectra in which each carbon signal appears as a singlet.
13C NMR Chemical Shift Table 1400 1200 130 110 215 200 1800 1650 60 10 800 600 70 40 95 80 60 30 70 40 800 550 1250 1150 220 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 ppm Alcohols Ethers Substituted Benzenes Alkenes Carbonyl. To distinguish between peaks whose assignment was ambiguous a further 1-2 µL of a specific substrate were added and the spectra run again. Overview of typical 1H NMR shifts 1H NMR Tables.
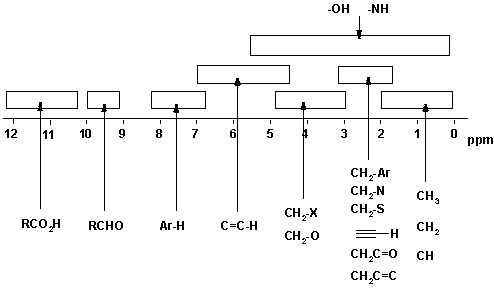
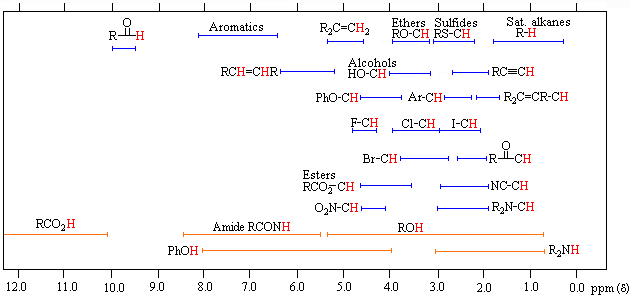
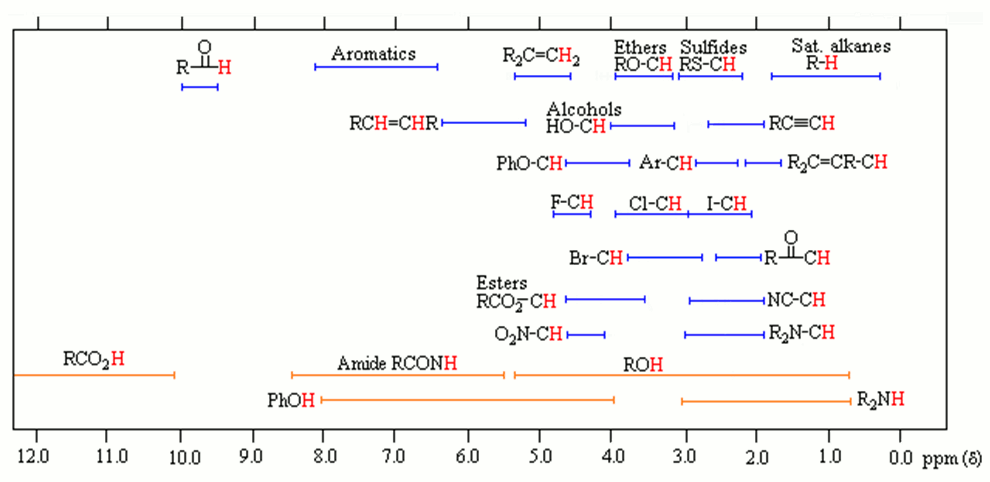
1H NMR Chemical Shifts 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 RH O H R 2CCR H ROCH 3 CH 3 RCH 3 O RH CH 3 CH NH OH RNH 2 O NH. Note the reduced ratio of the phenolic proton 1832047 t-butyl. Over the past fifty years nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy commonly referred to as nmr has become the preeminent technique for determining the structure of organic compounds.
D scale is relative to TMS at d0. Using NMR Chemical Impurities Tables. These splitting values are very useful and follow the N1N-1 rules the number of lines is one greater than the number of attached Hs.
The two peaks on the spectrum are located at d242 and d107Then expand it to be more clearThere are generally three possible ways for aromatic peaks to appear in a h nmr spectrum when only one group is attached the ringThere are two peaks on the graph therefore of the 10 hydrogens in the molecule there are two types. The water peak appears as two peaks a singlet corresponding to H 20 and a 111 triplet corresponding to HDO. The 1H spectra of the residual protons and 13C spectra were obtained on a Varian Gemini 200 spectro-meter at 295K.
This is a standard reference point with the signal set exactly at 0 ppm and y ou can ignore it when analyzing an NMR spectrum. The C H 3 peak splits into three peaks. NMR Chemical Shifts of Impurities Charts.
There are two peaks on the graph therefore of the 10 hydrogens in the molecule there are two types. This is the way our laboratory C13 NMRs come out. The only peak that comes before saturated C-H protons is the signal of the protons of tetramethylsilane CH3 4 Si also called TMS.
1 H NMR Chemical Shifts Table. H H H a b c Jac10 Hz Jcb2 Hz Jab15 Hz Ha Jab 15 Jac10 Hb Jab 15 Jbc2 Hc Jac10 Jbc2 In this example the splitting between protons a b and c does not follow the n1 rule because the coupling constants between all of these protons are different. For 1H NMR Vertical scale intensity of the signal Horizontal scale chemical shift d dependent upon the field strength of the external magnetic field.
The broad ranges shown at the bottom of the chart orange color are typical of hydrogen bonded protons eg. Usually the use of deuterated solvents enriched in 2 H instead of 1 H minimizes the size of solvent peaks in 1 H NMR. If a protic deuterated solvent is used eg D 2O or CD 3OD then the NH and OH protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or.
FROM TABLE 144 LABBOOK OR TABLE H6 SPEC BOOK FROM TABLE 146 LABBOOK OR TABLE H4 SPEC BOOK 58 50 52 61 701 Experimental sp2 IH chemical shifts ppm. However there is always a trace of 1 H left in the solvent which shows up as a small peak in. Home Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR NMR Chemical Shifts of Impurities Charts.
Has a spin of 1 triplets arising from. Figure 2- 1H NMR spectrum of 53 mg of 26-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol in DMSO-d 6 with 100 ppm D 2 O added. These tables can support you in identifying and separating NMR signals of impurities that might originate from residual solvents or from your.
The NMR solvents used to acquire these spectra. The peaks do not ovelap to give the appearance of a simpler spectrum. This is because there are 2 hydrogen atoms on the adjacent atom.
60 MHz for 1H 60 million hertz ppm 60 Hz 15 MHz for 13C 140000 gauss. For 1H d is usually from 1-10 ppm d 14100 gauss. So it becomes 213 peaks.
Ester Amide Carboxylic Acid Carbonyl. NMR Solvent data chart Solvent 1H Chemical Shift ppm from TMS multiplicity JHD Hz Carbon-13 Chemical Shift ppm from TMS multiplicity JCD Hz 1H. The chemical shifts were read and are presented in Table 1.
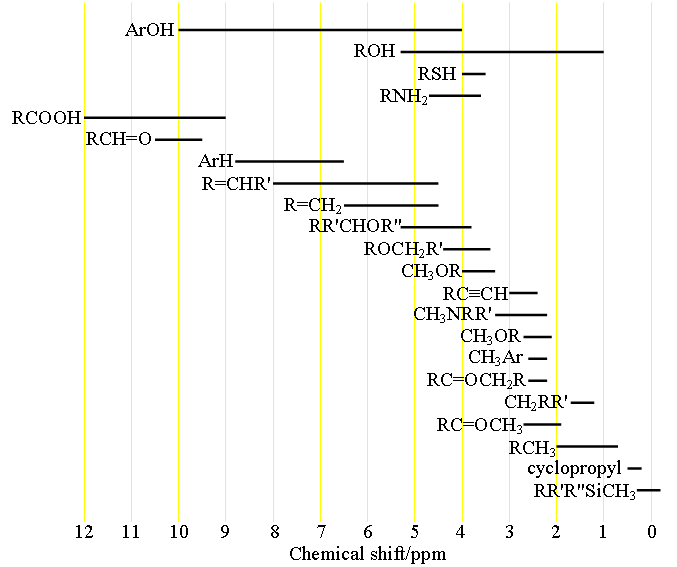
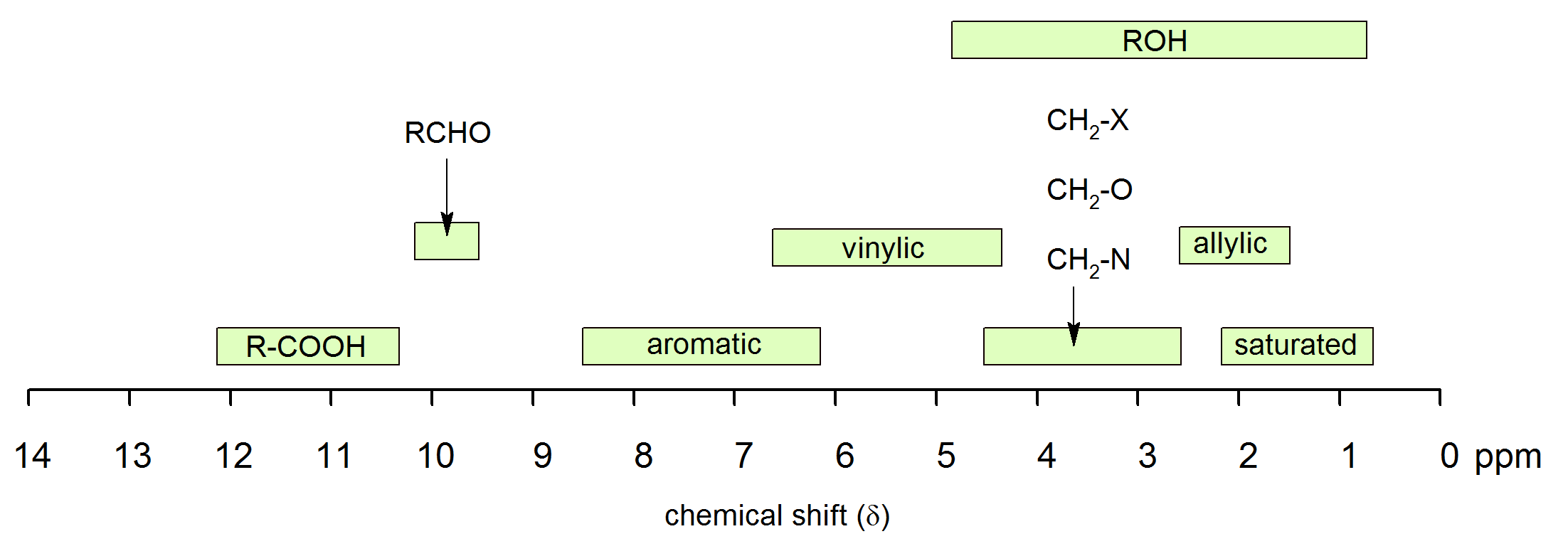
Proton Chemical Shift Ranges For. Unlike infrared and uv-visible spectroscopy where absorption peaks are uniquely located by a frequency or wavelength the location of different nmr resonance signals is dependent on both. However at the cost of extra time it is also possible to get coupled C13 NMRs with splitting.
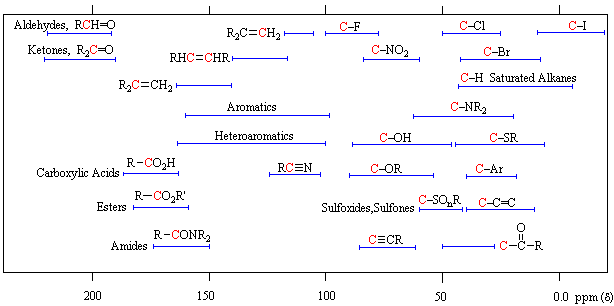
13 C Chemical Shifts Table. Aldehyde Ketone Alkanes Alkynes Amines Alkyl bromides Alkyl chlorides Alkyl fluorides CDCl. Organic Chemistry Michigan State University.
Note the single H 2 O peak at 33 ppm. 1H NMR Data proton mult CDCl 3 CD 3 2CO CD 3 2SO C 6D 6 CD 3CN CD 3OD D 2O solvent residual peak 726 205 250 716 194 331 479 H 2O s 156 284a 333a 040 213 487 acetic acid CH. In general protons follow the trend seen in the carbon to which they are attached.
Heckelman The Merck Index an Encyclopedia of Chemicals Drugs and Biologicals - Eleventh Edition Merck Co Inc.