Critical T Value Chart
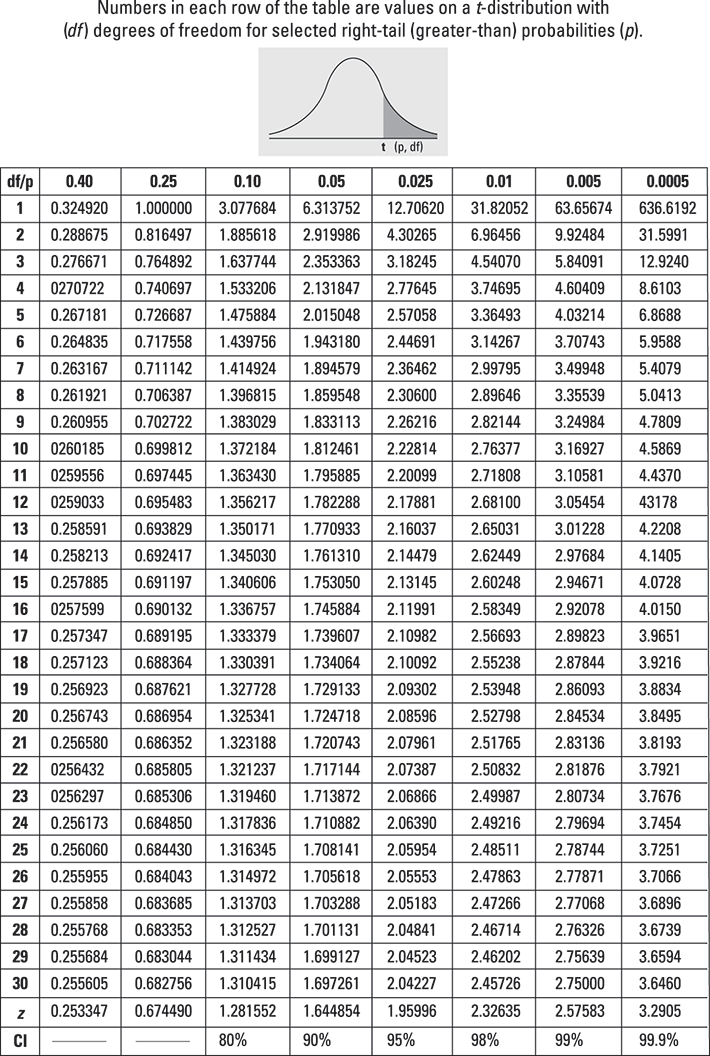
02 01 005 001 0005 0001 00005 00001 2 189 292 43 992 1409 316 447 10014 3 164 235 318 584 745 1292 1633 2801 4 153 213 278 46 56 861 1031 1553.
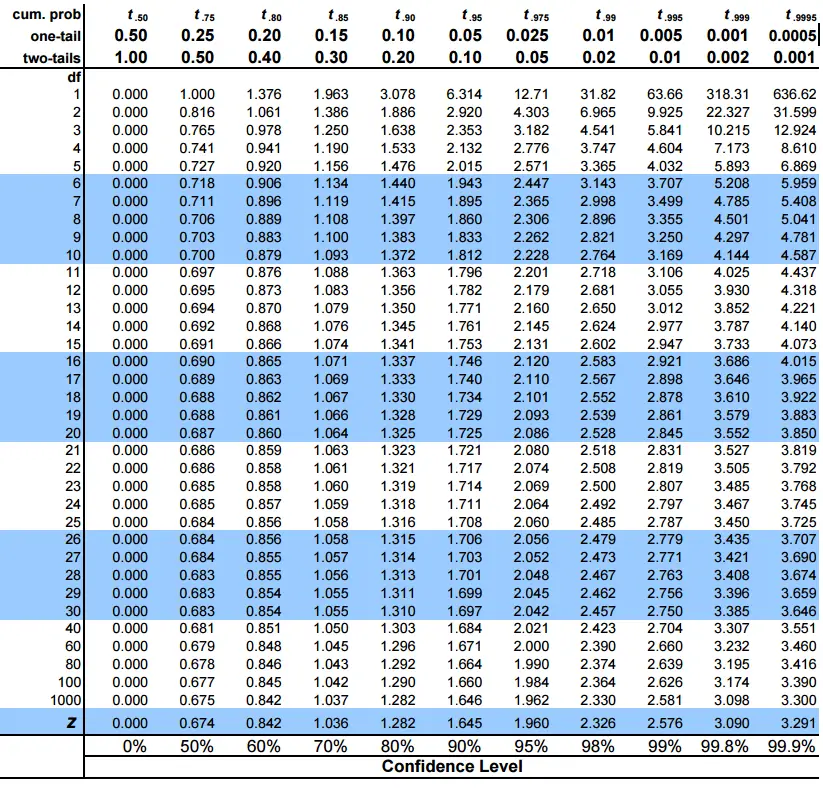
Critical t value chart. 90 95 98 99 1 631 1271 3182 6366 2 292 430 697 993 3 235 318 454 584 4 213 278 375 460 5 202 257 337 403 6 194 245 314 371 7 190 237 300 350. The t table can be used for both one-sided lower and upper and two-sided tests using the appropriate value of α. T critical value one-tailed 16978.
Even more T-statistic is. Critical value calculator with sample size. Critical value refers to the calculated critical value.
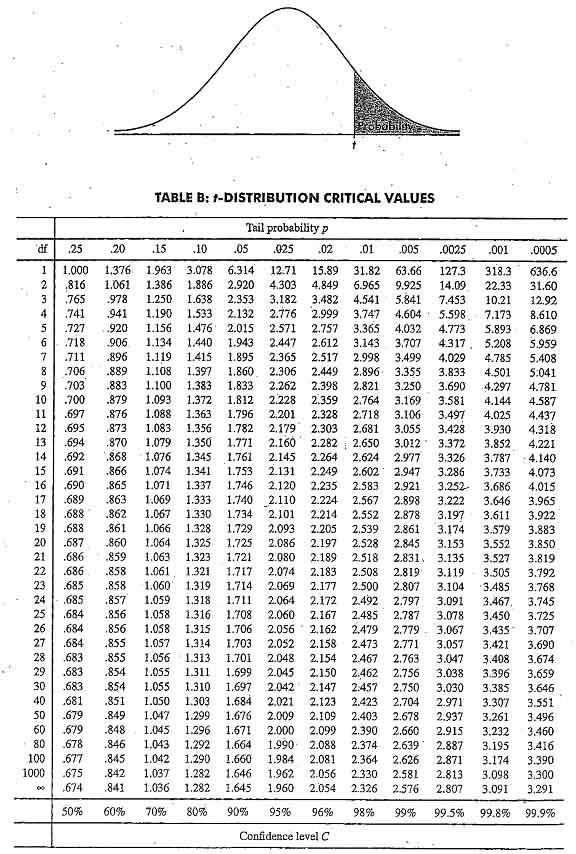
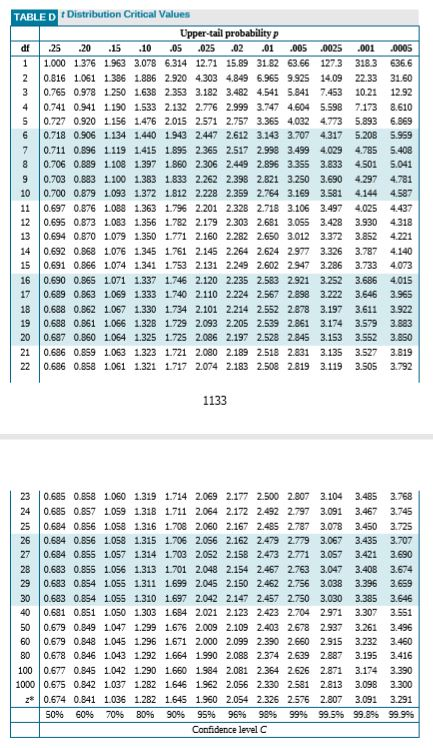
Critical Values for t-Interval. The second table gives critical values of F at the p 001 level of significance. The critical values of t distribution are calculated.
01 005 0025 0005 00025 00005 000025 000005 Two Tailed Significance level. 1 - 005 2 1 - 0025 0975 is the critical probability p. In this case the critical.
In the traditional version you use the t score table and alpha value to find the appropriate critical value for the test. We define a critical value for the test statistic using the context of probability and population distribution. Percent is distribution function - the table entry is the corresponding percentile.
The table entries are the critical values percentiles for the distribution. Lets calculate the. The values in the table are the areas critical values for.
The column headed DF degrees of freedom gives the degrees of freedom for the values in that row. Remember to adjust the alpha value to reflect the nature of the test - one sided or two sided. 203 rows Statistics - T-Distribution Table.
Get the corresponding value from table. Critical Values Tables 434 Table. X refers to the population observations.
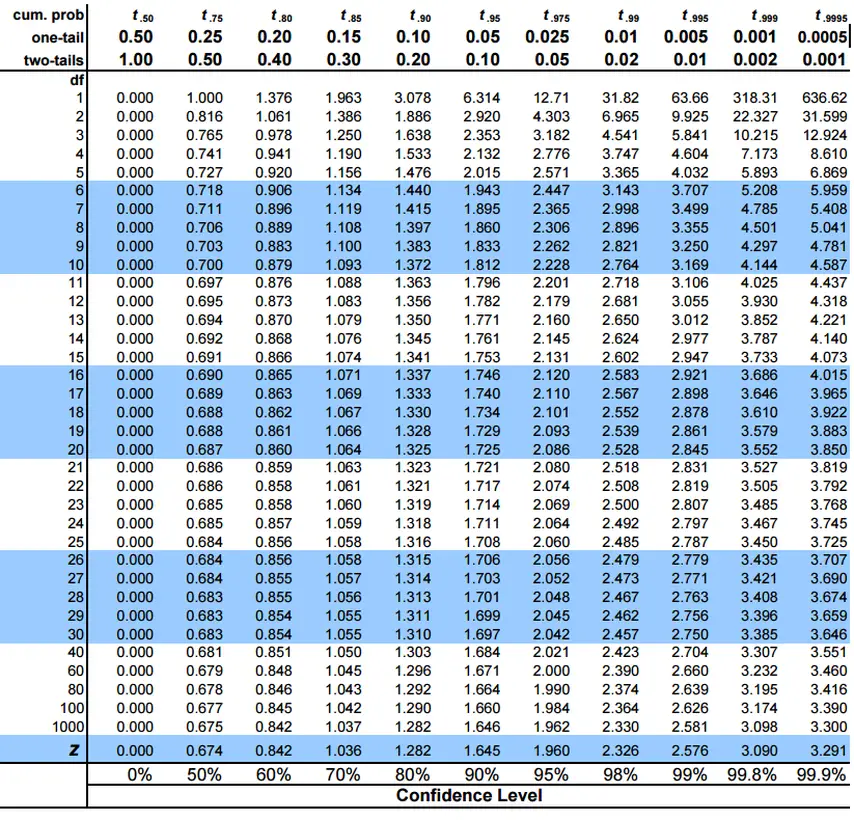
This has xy degrees of freedom associated with it. Pr refers to the probability calculation. How to Use This Table This table contains critical values of the Students t distribution computed using the cumulative distribution function.
For a t-test with one sample the degrees of freedom is equal to n-1 which is 20-1 19 in this case. The t distribution is symmetric so that t 1-αν -t αν. Go along x columns and down y rows.
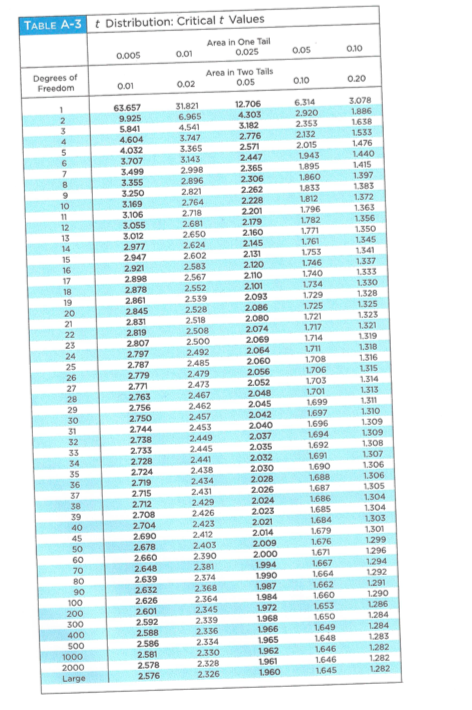
The columns are labeled by Percent. Critical tValues Area in One Tail 0005 001 0025 005 010 Degrees of Area in Two Tails Freedom 001 002 005 010 020 1 63657 31821 12706 6314 3078 2 9925 6965 4303 2920 1886. One Tailed Significance level.
How to find the critical value of t. One-sided is the significance level for the one-sided. 203 rows The critical values of t distribution are calculated according to the probabilities of.
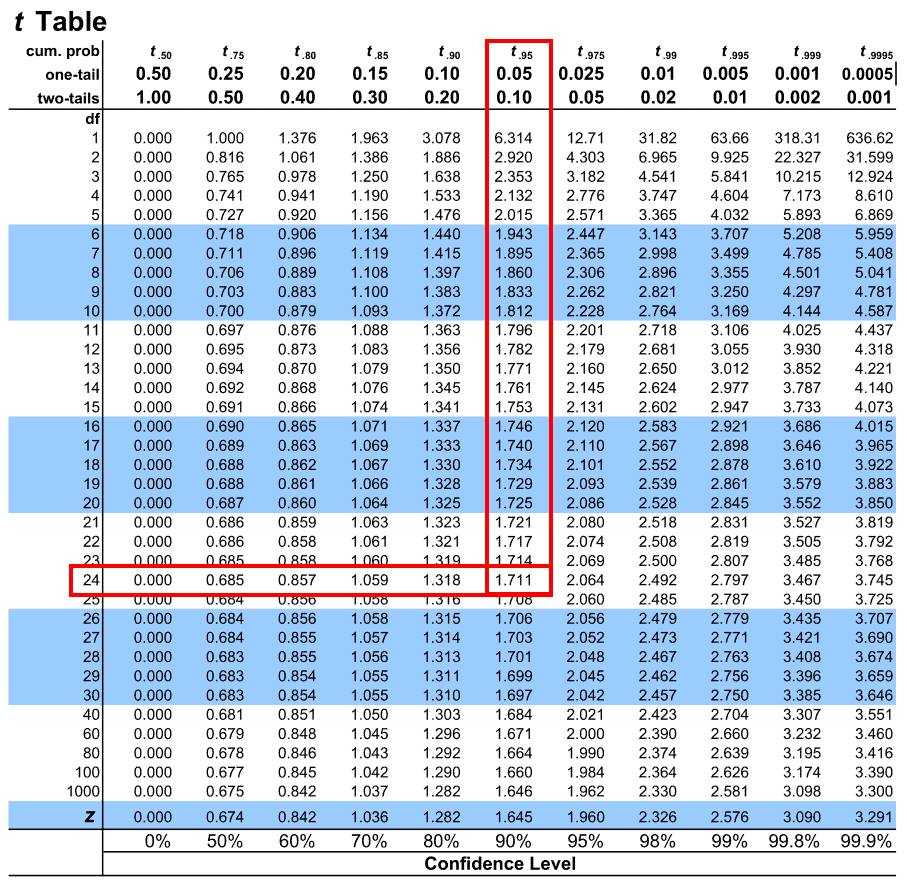
More information about critical values for the t-distribution. The critical t statistic is the right formulation for the critical probability when measuring a. The problem also tells us that she is conducting a one-tailed test and that she is using an alpha level of 005 so the corresponding critical value in the t-distribution table is 1729.
Critical t value negative a Left tail Critical t value positive a Right tail Critical t value positive Critical t value negative a2 a2 Two tails TABLE A-3 tDistribution. It can be mathematically expressed using the following formula. 27 rows The T Table stands for the critical values of T Distribution.
If your obtained value of F is equal to or larger than this critical F-value then your result is. 0 t critical value-t critical value t curve Central area t critical values Confidence area captured. How to use the Critical T-values Calculator.
Probability is 0975 or 975 percent. The point of intersection is your critical F-ratio. First of all critical values are points at the tail s of a specific distribution with the property that the area under the curve for those critical points in the tails is equal to the given value of.
PrX. 090 095 098 099 Confidence level.