A C-chart Is Based On The
For the control chart the size of the item must be constant.
A c-chart is based on the. C chart is one of the quality control charts used to track the number of defects in a. When applied to the c chart this implies that the mean of the defects should be at least 5. Then the lower control limit is 0513.
Normal A1c Levels Chart for Non-Diabetes. A c-chart is an attributes control chart used with data collected in subgroups that are the same size. C chart is also known as the control chart for defects counting of the number of defects.
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial or DCCT New England Journal. C-charts show how the process measured by the number of nonconformities per item or group of items changes over time. C chart takes into account the number of defects in each defective unit or in a given sample.
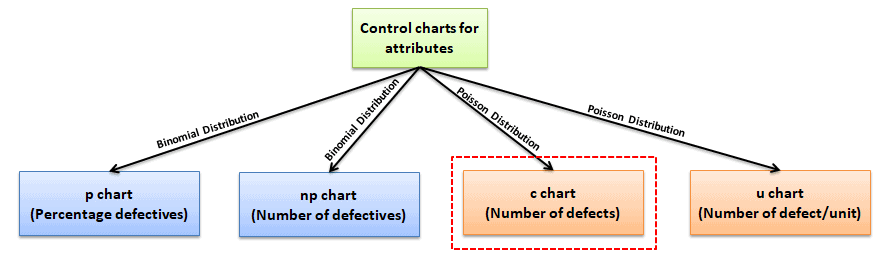
While p chart analyzes the proportions of non-conforming or defective items in a process. Because this formula derived from such a group. According to American Diabetes Association latest guidelines 2017 and 2018 Hemoglobin A1c levels 3 4 5 and up to 57 is normal and tell that the person has no DM.
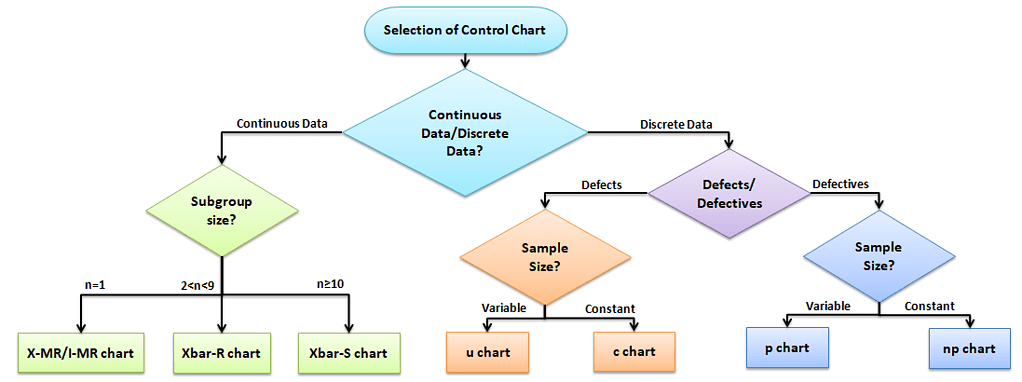
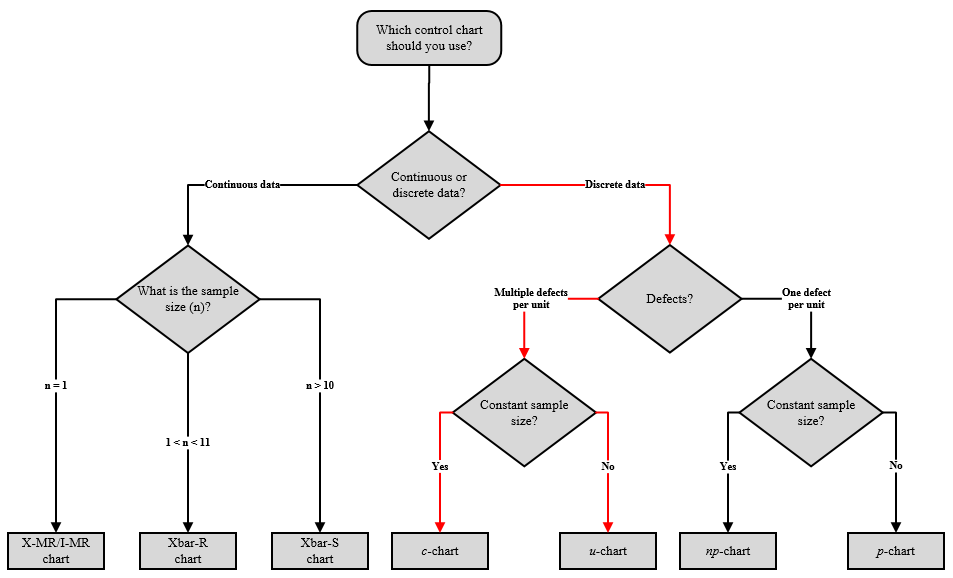
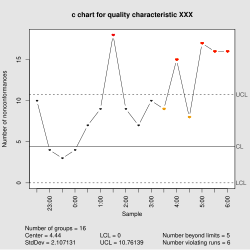
The plot shows the of defects. Control Charts for Discrete Data. C Control Charts C charts are used to monitor the number of nonconformities on a unit of a process based on units taken from the process at given times hours shifts days weeks months etc.
What are c charts. Let the mean be 10. This requirement will often be met in practice but still when the mean is smaller than 9 solving the above equation there will be no lower control limit.
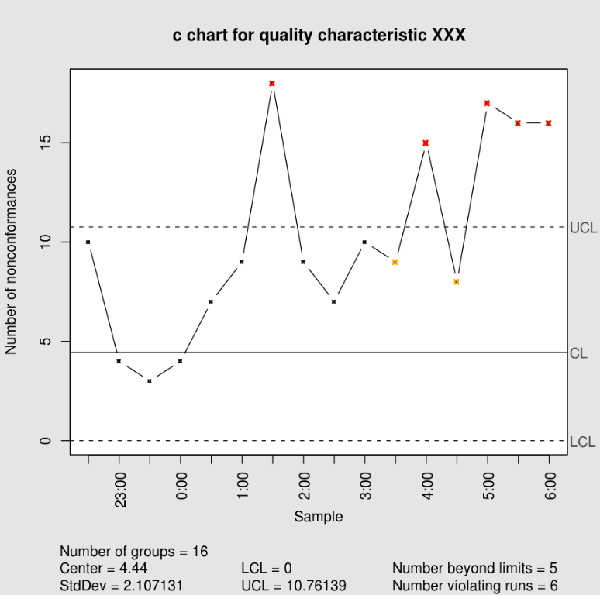
Click OK in each dialog box. Evaluates the stability of counted data. The number of defects is collected for the area of opportunity in each subgroup.
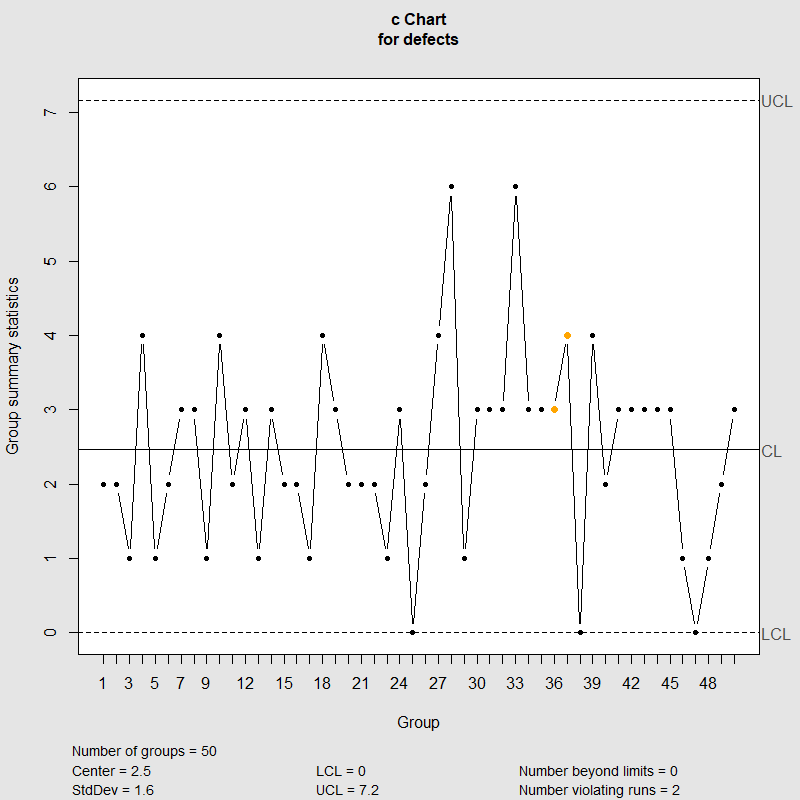
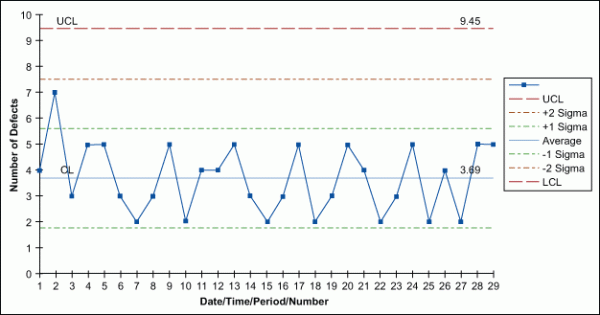
The average number of defects per sample is 3668. A c-chart is an attributes control chart used with data collected in subgroups that are the same size. Construction of c charts The c chart is based on the Poisson probability from CS 301 at SRM University.
Thus the process is out of control. Nonconformities are defects or occurrences found in the sampled subgroup. The number of defects c chart is based on the Poisson distribution.
However Pc0 0000045 using the Poisson formula. Example of C Chart. The item may be a given length of steel bar a welded tank a bolt of cloth and so on.
This is only 130 of. A c chart or Count chart is an attribute control chart that displays how the number of defects or nonconformities for a process or system is changing over time. A1C level chart in this article shows the relationship between A1C and its average blood sugar equivalent based on the DCCT A1C conversion formula.
It is a plot of the number of defects in items. It is generally used to monitor the number of defects in constant size units. DCCT A1C conversion formula seems to work best in people with high blood sugars.
When to Use c Chart. C chart the number of defects is plotting on the y-axis and the number of units on the x-axis. Nonconformities are defects or occurrences found in the sampled subgroup.
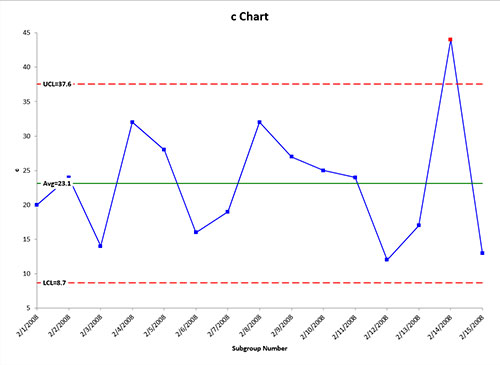
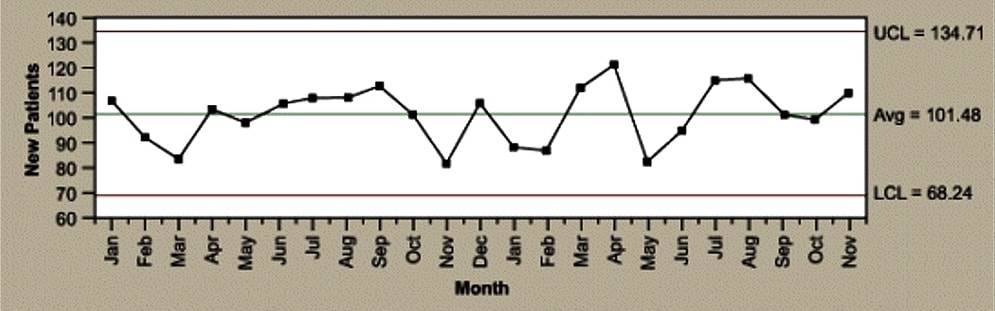
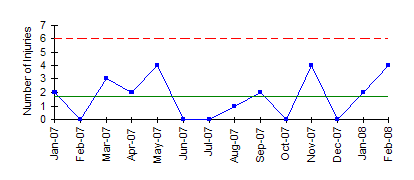
Samples 12 and 13 failed Test 1 because they are outside the control limits. This chart is used when the number of samples of each sampling period is essentially the same. C-charts show how the process measured by the number of nonconformities per item or group of items changes over time.
Sorting all hemoglobin Hgb A1c levels for each diabetic condition based on DCCT formula Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Typically an init ial series of units is used to estimate the average number of nonconformities of a process. The c chart is for the number of defects in an item.
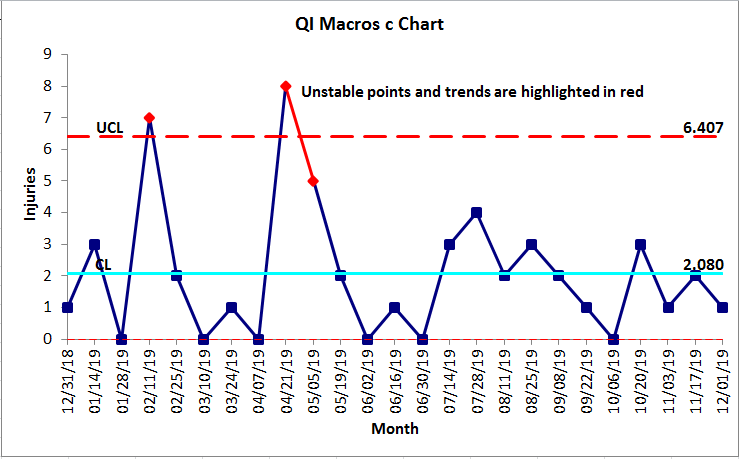
The engineer should identify and correct any factors that. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit c that occurred during the sampling period the c-chart allows the practitioner to assign each sample more than one defect.